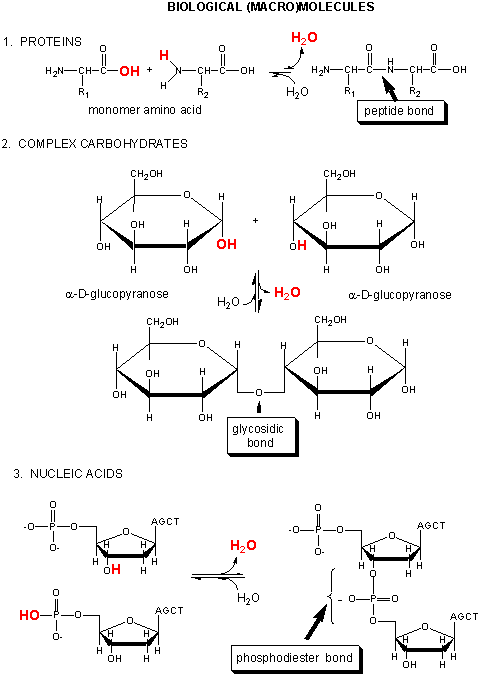
Proteins are covalent polymers of amino acids. They are much more complicated than
most lipids, since different proteins differ not only in the number of amino acids but also the sequence. Compare this
to the intermolecular aggregates of lipids which for the most part can be characterized as containing distinct hydrophobic
and hydrophilic regions. Remember, as with other biological polymers, proteins form from a covalent attachment of the
amino end of one amino acid with the carboxy end of another, with release of water. This later trait also occurs on
formation of proteins and nucleic acids.
During our study of proteins we will try to understand both the structure and function of
the protein. We can gain understanding of proteins using both low and high resolution techniques, as illustrated in the figure
below, which introduces how we will start our study of proteins.

